Resultant Force
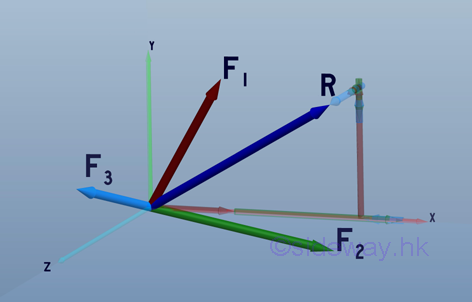
The resultant force of concurrent forces in space can be represented by a force vector, R, in three dimensional space.
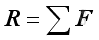
The most practical way of determining the resultant force in space is to add up their rectangular components respectively:
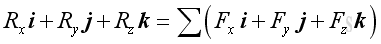
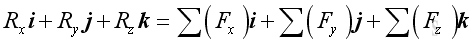
Imply:
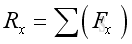
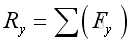
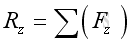
Therefore:
And similarly, the resultant force vector, R, can be expressed as:
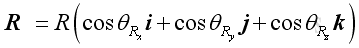
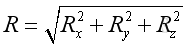
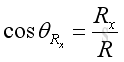
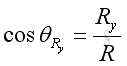
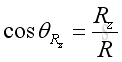
Force Equilibrium
According to Newton's first law of motion, when a particle is in equilibrium, the resultant of all the forces acting on it is zero. That is
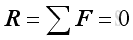
And graphically in the form of force polygon,
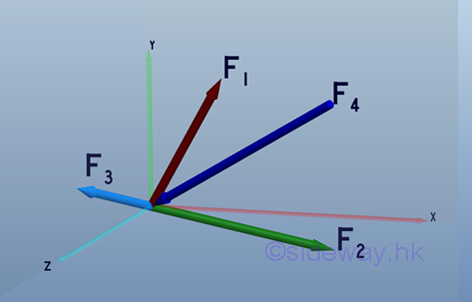 , imply
, imply
©sideway
ID: 110400007 Last Updated: 5/28/2011 Revision: 1 Ref:
References
- I.C. Jong; B.G. rogers, 1991, Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Dynamics
- F.P. Beer; E.R. Johnston,Jr.; E.R. Eisenberg, 2004, Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
Latest Updated Links
- Ikea SANDSBERG table(last updated On 11/4/2025)
- Ikea TISKEN toilet roll holder(last updated On 11/3/2025)
- Philips CL400 Ceiling Light 36W(last updated On 11/2/2025)
- Philips CL400 Ceiling Light 24W(last updated On 11/1/2025)
- Philips CL400 Ceiling Light 13W(last updated On 10/30/2025)
- Ikea TISKEN basket(last updated On 10/29/2025)
- Ikea TISKEN towel rack(last updated On 10/28/2025)
- Ikea REXBEGONIA mattress protector(last updated On 10/27/2025)
- Ikea KEJSAROLVON mattress protector(last updated On 10/26/2025)
- Ikea KVARNVEN ergonomic pillow(last updated On 10/25/2025)
- Ikea BRUKSVARA pocket prung mattress(last updated On 10/24/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 8
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 18
Reference 79
Hardware 27![]()
Computer
Hardware 259
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1
